When it comes to improving your health, energy levels, and overall well-being, it often comes up as a go-to solution.
Whether you’re feeling fatigued, experiencing mental fog, or dealing with a deficiency, Vitamin B12 supplementation can help. But one common question many people ask is, “How long does it take to work?” The truth is, the timeline for results can vary depending on factors like your. How long does it take for Vitamin B12 to work
In this article, we’ll dive deep into how it works in the body and what influences the process. You’ll also discover practical tips to optimize your intake and feel the benefits sooner.

What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in your overall health. It is vital for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system, and is involved in the production of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 helps in synthesizing DNA and supports metabolic functions, particularly in converting food into energy.
This unique vitamin is distinguished by its mineral content—cobalt—which is why it’s also referred to as cobalamin. It is naturally found in animal-based foods like meat, eggs, fish, and dairy, and plays a crucial role in several bodily functions.
Key Functions of Vitamin B12
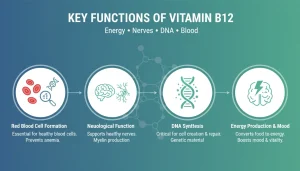
1. Supports the Nervous System
B12 is essential for maintaining the health of your nerve cells. It plays a key role in the production of myelin, a fatty substance that coats and protects nerve fibers, ensuring proper electrical signal transmission. Without enough B12, nerve function can be impaired, leading to symptoms like tingling sensations, numbness, and poor coordination. If left untreated, a severe deficiency can result in permanent nerve damage.
2. Mental Clarity and Brain Function:
Vitamin B12 supports cognitive function by aiding in the production of neurotransmitters—chemical messengers in the brain. When B12 levels are low, it may lead to memory issues, brain fog, and even mood disorders such as depression. Maintaining optimal B12 levels may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
3. Red Blood Cell Production:
B12 plays an essential role in the formation of red blood cells. It aids in synthesizing DNA, ensuring the proper development and function of red blood cells. Deficiency in B12 can lead to megaloblastic anemia, where the red blood cells are abnormally large and inefficient in carrying oxygen, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
4. Energy Production:
By helping metabolize fats and proteins, Vitamin B12 is essential in converting food into energy. When your body is low on this vitamin, you may feel fatigued and drained, as it becomes harder to convert food into usable fuel.
5. Immune System Support:
Vitamin B12 is also critical for a strong immune system. It aids in the production and activation of white blood cells, which help protect your body from infections and diseases. A deficiency in B12 can make your immune response weaker, making you more vulnerable to illnesses.
How Does the Body Absorb Vitamin B12?
When you consume B12-rich foods, it is released in the stomach with the help of digestive acids and enzymes. The vitamin then binds with a protein called intrinsic factor (IF) produced by the stomach. This complex travels to the small intestine, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream and carried to the cells that need it.
However, this absorption process can be hindered by several factors, such as age, digestive issues, or medications that interfere with the body’s ability to absorb B12. For this reason, many individuals, particularly older adults or those with gastrointestinal issues, may require supplements or injections to ensure they’re getting enough of this vital nutrient.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal-based foods, making it easier for individuals who consume meat, dairy, eggs, and fish to get adequate amounts. Common food sources include:

- Meat (beef, pork, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Fish and shellfish (salmon, tuna, shrimp)
- Eggs
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
For vegans or vegetarians, it’s essential to either consume fortified foods (such as plant-based milks, fortified cereals, and nutritional yeast) or take B12 supplements to prevent deficiency.
Who Is at Risk for Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Certain groups of people are more vulnerable to Vitamin B12 deficiency, including:
- Older Adults: The body’s ability to absorb B12 decreases with age, increasing the risk of deficiency.

- People with Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and gastritis impair B12 absorption.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: These women require more B12 for both their health and the health of their babies.
- People on Certain Medications: Some medications, such as proton pump inhibitors or Metformin, can interfere with B12 absorption.
How Long Does It Take to Work and Show Results
The time it takes for Vitamin B12 to show results depends on several factors, including the form of supplementation, your body’s current B12 levels, and the specific symptoms you’re targeting. Here’s a breakdown of what to expect:
For Energy:
People dealing with fatigue may start noticing an energy boost within a few hours of taking a B12 shot or sublingual supplement. Oral supplements may take longer—usually around 3-4 hours for the vitamin to enter circulation. However, the time it takes can vary depending on individual digestion and absorption rates.
For Mental Clarity:
It can take a few days to several weeks to notice improvements in mental clarity and mood. Many people experience a reduction in brain fog and increased alertness after consistent B12 supplementation. This is particularly true for individuals who have experienced cognitive decline or mental fatigue due to low B12 levels.
For Red Blood Cells:
If you’re addressing megaloblastic anemia, it may take about a week or more to see improvements in red blood cell production, which can alleviate symptoms such as dizziness,
Weakness, and shortness of breath. Over time, as your red blood cells become more efficient, you should feel more energized and less fatigued.
Types of Vitamin
B12 Supplements: What Works Best?
Not all Vitamin B12 supplements are the same, and choosing the right form can influence how quickly and effectively the nutrient is absorbed. Here’s a breakdown of common forms of B12 supplementation:
Cyanocobalamin:
This synthetic form of B12 is commonly used in supplements. It’s affordable and effective for most people, but it needs to be converted by the body into an active form, which can be a slower process for some individuals.
Methylcobalamin:
Methylcobalamin is an active form of B12 that doesn’t require conversion. This makes it a better choice for those who may have difficulty converting cyanocobalamin into its active form. It’s often preferred for quicker absorption.
Sublingual B12:
Sublingual B12 is absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes under your tongue, bypassing the digestive system. This can be an effective option for people with digestive issues that impede proper B12 absorption.
B12 Injections:
For immediate and significant increases in B12 levels, injections are often used. They can lead to rapid boosts in energy and are typically recommended for people with severe deficiencies or absorption issues.
How to Ensure You’re Getting Enough Vitamin B12
If you’re not getting enough B12 from your diet, it’s essential to either incorporate more B12-rich foods or take supplements. For those following a vegan or vegetarian diet, fortified foods or supplements are the best way to meet daily needs.
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12 varies based on age, lifestyle, and specific health conditions. Consult your healthcare provider to determine your needs and avoid unnecessary supplementation.
Conclusion
Now that you know how long it takes for Vitamin B12 to work, you can supplement confidently. Vitamin B12 is a powerful nutrient that plays a vital role in many body functions, from energy production to cognitive health and immune support. How long it takes to feel its effects depends on a variety of factors, such as your current B12 levels, the form of supplementation, and how well your body absorbs the vitamin.
By ensuring you’re getting enough B12 through your diet or supplements, and considering your individual health circumstances, you can optimize your chances of feeling the benefits sooner.
FAQs
- Can I take too much Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is water-soluble, meaning that excess amounts are typically excreted in the urine. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- How can I tell if I’m getting enough B12 in my diet?
If you’re experiencing symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, or tingling sensations, it may be a sign of deficiency. A blood test can confirm your B12 levels.
- What are the best food sources for Vitamin B12?
The best sources of Vitamin B12 are animal-based foods like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. For vegans, fortified foods or supplements are essential.
